Editorial Note:
This article on conflict theory, structural functionalism, and symbolic interactionism is being published on behalf of Applied Worldwide’s student essay competition. Students were prompted to respond to the question, “Why is sociology important?” We have awarded 16 finalists from all over the world, and we published these essays over the course of a few weeks.
This essay was written by Hassan Idris, a student at Ahmadu Bello University in Nigeria. This essay received a third place award. We had a really great turnout and would like to thank everyone who submitted an essay. We received a wide variety of creative interpretations and responses, so browse our essay directory!
Hassan Idris – Conflict Theory, Structural Functionalism, and Symbolic Interactionism
Sociology is the scientific study of the society and its various elements. Before the emergence of sociology, society had never been the major concern and its study was carried in a very unscientific manner. But, things have altered in the present scenario. Sociology has emerged to be of great importance because of its impact on individuals and the society. It is the key study for the present situation. A person who is engaged in the study of sociology is referred to as a sociologist. As society is a complex structure, the study of sociology is required in each and every step of life.
However, there are various founding fathers of Sociology such as, Auguste Comte, Karl Heinrich Marx, David Emile Durkheim, Herbert Spencer and many more. I will start from the modern founding father who first coined the discipline, Auguste Comte.
The Founding of Sociology
The French philosopher Auguste Comte (1798–1857)—often called the “father of sociology”—first used the term “sociology” in 1838 to refer to the scientific study of society. He believed that all societies develop and progress through the following stages: religious, metaphysical, and scientific.
Comte argued that society needs scientific knowledge based on facts and evidence to solve its problems—not speculation and superstition, which characterize the religious and metaphysical stages of social development. Comte viewed the science of sociology as consisting of two branches: dynamics, or the study of the processes by which societies change; and statics, or the study of the processes by which societies endure.
He also envisioned sociologists as eventually developing a base of scientific social knowledge that would guide society into positive directions (Maccionis, 1947).
Herbert Spencer
The 19th‐century Englishman Herbert Spencer (1820–1903) compared society to a living organism with interdependent parts. Change in one part of society causes change in the other parts, so that every part contributes to the stability and survival of society as a whole. If one part of society malfunctions, the other parts must adjust to the crisis and contribute even more to preserve society. Family, education, government, industry, and religion comprise just a few of the parts of the “organism” of society (Ritzer, 1991).
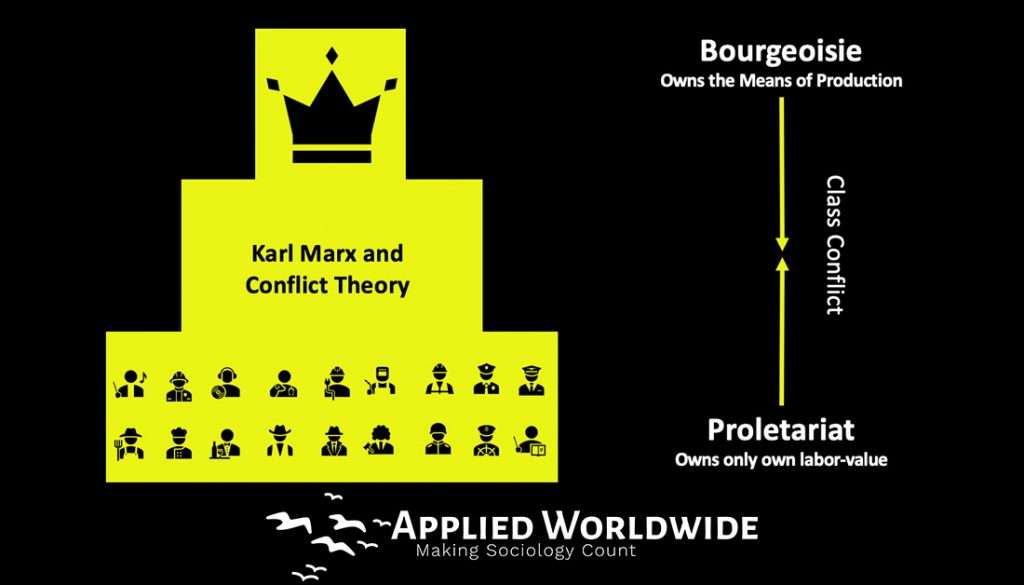
Karl Marx and Conflict Theory
The German political philosopher and economist Karl Marx (1818–1883), who observed society’s exploitation of the poor by the rich and powerful. Marx claimed that social conflict, especially class conflict, and competition mark all societies.
The class of capitalists that Marx called the bourgeoisie particularly enraged him. Members of the bourgeoisie own the means of production and exploit the class of laborers, called the proletariat, who do not own the means of production. Marx believed that the very natures of the bourgeoisie and the proletariat inescapably lock the two classes in conflict.
But he then took his ideas of class conflict one step further: He predicted that the laborers are not selectively “unfit,” but are destined to overthrow the capitalists. Such a class revolution would establish a “class‐free” society in which all people work according to their abilities and receive according to their needs (Ritzer, 1991).
Sociology and the Nature of Man
Sociology is very important because Sociology tells us more about the social nature of man. As we already know, sociology is the scientific study of humans and the society they live in. Sociology throws light on the relationship between individuals and society.
Sociology plays a vital role in the solution of international problems. The political division of the world usually gives rise to conflict and stress among nations. Sociology, thus, tries to understand the underlying cause of tensions and initiates peace among nations.
Sociology is the base of planning of society—it is the foundation on which the planning of society lies. Before implementing any social policies, a specific amount of knowledge regarding the society is essential.
Sociological Knowledge
The knowledge of sociology would assist in the process of understanding the relationship between economy and religion, society and individuals. We could understand the recent novel coronavirus pandemic in the world and how it’s affecting the world social relationships, industries and bureaucratic organizations as Max Weber calls it “the iron cage”. The holistic approach adopted by Sociology could help us understand the world general social problems in relation to one another; relationship of COVID-19 to religion, politics, economy, law and many more.
Big Three Sociological Theories Including Conflict Theory
I adopted three sociological perspectives in explaining and solving real world problem: conflict perspective, functionalism and interactionism.
From the Conflict Theory, spearheaded by Karl Heinrich Marx which claimed that social conflict, especially class conflict, and competition mark all societies. We could understand that amidst this coronavirus pandemic, the ruling classes are the ones benefiting from this novel virus pandemic. In the global world today, the ruling classes have been siphoning billions of naira all in the name of curbing this novel virus.
With the knowledge of sociology we could understand and solve all these problems, since we have understood the problem, solution will be easy. The capitalists keep searching for ways to exploit and get more capital and surplus values amidst this coronavirus pandemic. This is why Karl Marx said in his Das Kapital that “capital is dead labor, which, vampire-like, lives only by sucking living labor, and lives the more, the more labor it sucks.”
Structural Functionalism
The functionalist perspective spearheaded by Auguste Comte, Emile Durkheim, etc. emphasized the social structure and the social system; the interconnection and equilibrium. If one part among the social system is affected, it will affect other social systems thereby hindering the smooth running of the social structure. We have seen how the world has come together to approve lockdown and isolation to minimize the spread of this novel corona virus. In the social world, without functionalism, the world will be hectic as all must come together to make a change.
Symbolic Interactionism
The interactionists spearheaded by Max Weber and others emphasized the interactions in the social world as the main catalyst of change encouraging social interactions. Well, we have seen in world at large how this corona virus pandemic have reduced social interactions between people. We have also seen how the ethics of some religious leaders have made their followers not to believe in the existence of coronavirus as the protestant ethics and the spirit of capitalism of Max Weber made us to understand how religious ethics paved ways for the rise of capitalism.
Final Thought on Sociological Theories Including Conflict Theory and Others
In conclusion, sociology is very important in the understanding of the social world we are today.







